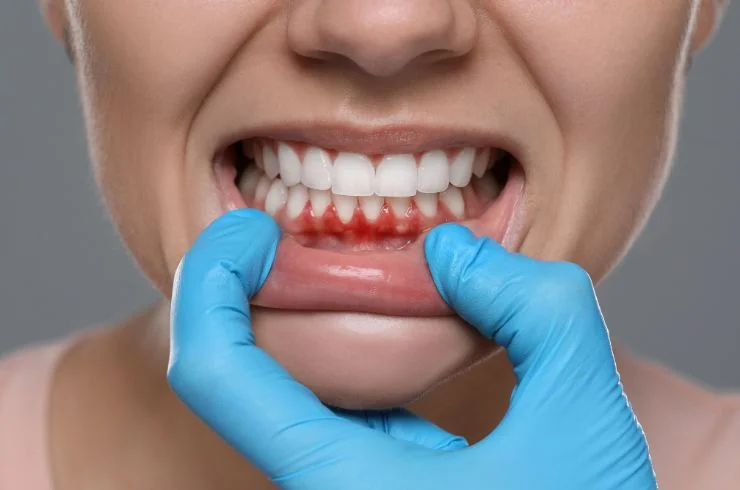
What is Gum Treatment?
Gum treatment, often referred to as periodontal therapy, encompasses a range of procedures aimed at preventing, diagnosing, and treating gum disease (periodontal disease). Healthy gums are crucial for overall oral health, as they support the teeth and play a significant role in preventing tooth loss. Gum treatment is designed to restore gum health, alleviate symptoms, and promote overall oral hygiene.
Indications for Gum Treatment
Patients may require gum treatment for several reasons, including:
Types of Gum Treatments
Non-Surgical Treatments: These are often the first line of defense against gum disease.
Surgical Treatments: If non-surgical methods are insufficient, surgical options may be considered.
Benefits of Gum Treatment
Who Should Consider Gum Treatment?
Individuals exhibiting symptoms of gum disease, such as swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or loose teeth, should seek evaluation and treatment from a dental professional. Regular dental check-ups can help identify gum issues early on, allowing for timely intervention.
Considerations and Aftercare
In summary, gum treatment is a vital aspect of dental care that focuses on preserving gum health and preventing more severe dental issues. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can lead to improved oral health, aesthetics, and overall well-being.