Abscesses and cysts in the mouth can cause significant pain, swelling, and discomfort. An abscess is a pocket of pus caused by infection, typically due to tooth decay, gum disease, or injury. A cyst, on the other hand, is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the jaw or around teeth, often leading to complications if left untreated. Both conditions can lead to serious oral health issues, including infection spread, bone damage, or tooth loss. Removal of abscesses and cysts is essential to prevent further damage, relieve pain, and restore oral health through surgical or non-surgical interventions.
Treatment for abscesses and cysts generally involves removal to prevent further complications. The method of removal depends on the type, size, and location of the abscess or cyst.
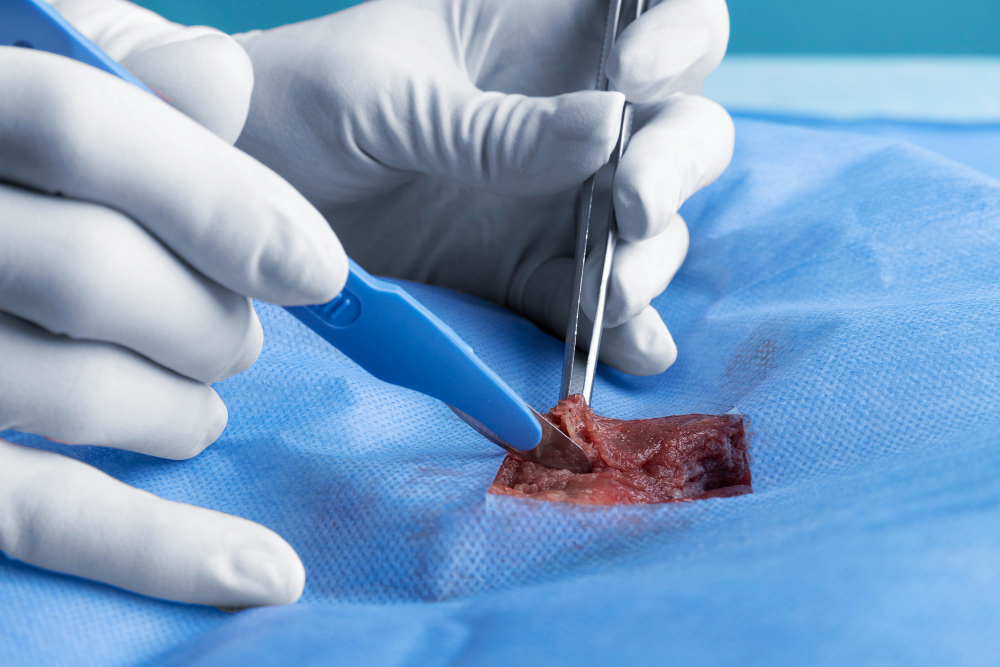
Draining the Abscess: The primary treatment for abscesses is draining the pus, which may be done by making a small incision. This helps to alleviate pressure, relieve pain, and allow for healing. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia.
Root Canal or Tooth Extraction: If the abscess is caused by infection in the tooth, the dentist may perform a root canal to remove the infected pulp and seal the tooth. In more severe cases, the affected tooth may need to be extracted.
Antibiotics: If the infection has spread or is severe, antibiotics may be prescribed to control the infection and help clear it before or after the abscess is drained.
Pain Management: Pain relief, including over-the-counter medications or prescribed painkillers, is often part of the treatment to reduce discomfort following the procedure.
Surgical Removal: Most cysts, particularly those causing pain or damage, require surgical removal. The dentist or oral surgeon will make an incision to access and remove the cyst, including its capsule. In some cases, surrounding bone or tissue may need to be removed if the cyst has caused significant damage.
Enucleation: This is the complete removal of the cyst, ensuring the entire cyst and its lining are taken out to prevent recurrence.
Post-Surgical Care: After removal, follow-up care is crucial for healing. This may involve monitoring the area, keeping it clean, and attending follow-up appointments to ensure no infection or complications arise.
Abscess and cyst removal is necessary in several situations, including:
Abscesses: If an abscess is causing pain, swelling, or fever, draining and treating the infection are critical. Untreated abscesses can lead to the spread of infection to other parts of the body, including the bloodstream, which may lead to more severe health issues.
Cysts: If a cyst is causing discomfort, swelling, or pressing on nearby structures, removal is recommended. Even if a cyst is asymptomatic, it can still cause damage to surrounding tissues and bone over time, necessitating its removal.
In both cases, treatment may be required when other, less invasive methods fail to resolve the problem or prevent further complications.
Removing abscesses and cysts provides multiple health benefits:
While abscess and cyst removal is generally safe, there are some potential risks:
Proper aftercare is essential to ensure healing and prevent complications:
Abscess and cyst removal is an important procedure to maintain oral health and prevent further complications. Whether treating an abscess caused by infection or removing a cyst that is causing discomfort or damage, timely intervention ensures a smooth recovery and prevents long-term oral health issues. If you notice pain, swelling, or other symptoms that may indicate an abscess or cyst, it’s crucial to consult with your dentist or oral surgeon. They can determine the best course of treatment to relieve symptoms, preserve the health of your teeth and jaw, and restore your overall well-being.